Snehadhya Charak Samhita Sutrasthan 13th Chapter: Snehakarma
Before starting with Panchakarma treatment, Snehakarma (Oiling treatment) and Swedana (sweating treatment) is done. Panchakarma is a method of expelling the imbalanced Doshas out of the body. Before they are expelled either by oral or anal route, the imbalanced Dosha needs to be softened, mobilized and brought into the gastro-intestinal tract for easy evacuation of imbalanced doshas. This is achieved by Snehakarma and Swedakarma. This chapter, the 13th of Sutrasthana of Charak Samhita explains Snehakarma in full detail.
Once upon a time, Lord Punaravasu was sitting with scholars. Agnivesha put forth a few doubts before Punarvasu, for the sake of the well being of the universe.[3]
Table of Contents
Questions regarding oils and fats
- What are the sources of Sneha Dravya – unctuous (oily) substances?
- What are the types of unctuous substances?
- What are the qualities of different oily substances?
- What are the appropriate times and Anupana (substance to be taken with or after the intake of medicine) for administering different types of oily substances?
- What and how many are the recipes of unctuous substances?[4]
- What are the different types of dosage?
- What are the measures?
- Which specific dose is prescribed for whom?
- Which oily substance is beneficial for whom?
- What are the maximum and minimum durations of Snehakarma (oleation)?[5]
- What are the indications and contra- indications for oleation?
- What are the features of proper oleation, non-oleation and excessive oleation?
- What is beneficial and what is harmful before and after the intake of fats, and also after its complete digestion?[6]
- What are the features of Mrdukostha (laxed bowel / soft bowel) and Krurakostha (hard bowel)?
- What are the complications of oleation therapy and what are their managements?
- What is the regimen prescribed during oleation therapy of both types administered for elimination or as palliative measure?[7]
- What recipes should be given to whom and how are they to be prepared?
I want to know all these about oils and fats, O my Lord![8]

Sources of oils and fats
Sneha Yoni – Sources of oils and fats
Lord Punarvasu replied, “There are two sources of oils and fats viz, vegetable and animal” [9]
Plant sources
Vegetable sources – Sthavara Yoni of Sneha –
Tila – Sesame (Sesamum indicum), Priyala (Buchanania lanzan), Abhishuka (Pistacia vera Linn),
Bibhitaki (Terminalia belerica Roxb), Chitra – Baliospermum montanum,
Abhaya – Terminalia chebula, Eranda – castor (Ricinus communis Linn),
Madhuka– Madhuca indica, Sarshapa – mustard (Brassica nigra Koch),
Kusumbha (Carthamus tinctorius Linn), Bilva – (Aegle marmelos Corr),
Aruka (Prunus persica Linn) Mulaka – Radish – (Raphanus sativas Linn0),
Atasi – Linseed (Linum usitatissimum Linn), Mikocaka(Artocarpus lakoocha Roxb),
Akshoda (Aleurites moluccana Willd), Karanja (Pongamia pinnata Merr), and
Shigruka (Moringa oleifera Lam).
These are the vegetable sources of oil.
Animal sources
Animal fat – Jangama Yoni of Sneha – is contributed by – The fish, quadrupeds and birds.
Curd, milk, ghee, meat, Muscle, fat and bone marrow of these animals and birds are administered as oily substances.[10-11]
Properties of Sesamum oil and castor oil
Of all the varieties, Tila taila – sesame oil is the most efficacious for the purpose of strength and oiling the body;
Eranda – castor oil is the best oil for purgation.
Castor oil is Katu (pungent), hot and heavy to digest.
Castor oil balances Vata and Kapha. But when mixed up with herbs possessing astringent, sweet and bitter tastes, it alleviates pitta as well.[12]
Types of unctuous substances
Types of Sneha Dravya – unctuous substances:
Ghrita – Ghee,
Taila – oil,
Meda (Vasa) – muscle fat and
Majja – Bone marrow
These are the best fatty substances of all. Among them ghee is the best oily substance, because of its power to assimilate effectively the properties of other substances. (Samskara Anuvartana)

Medicinal properties of ghee
Ghee balances Pitta and Vata.
It is conducive to Rasadhatu, Sukradhatu (semen) and Ojas. It has cooling and softening effect on the body. It adds to the clarity of the voice and complexion.[14]
Properties of Taila – oils
Oil alleviates Vata, it does not aggravate Kapha, it promotes body strength.
It controls the morbidity of the female genital organs.[15]
Properties of Vasa – fat
The fat is prescribed for the treatment of injury, fracture, trauma, uterine prolapse, earache and headache. It enhances the virility of a person. It helps in oleation and is ideal for those who do daily exercise. [16]
Properties of bone marrow
The (bone) marrow enhances strength, Shukra(male and female reproductive system), Rasadhatu, Kapha Dosha, Medodhatu(fat) and Majja(marrow). It improves strength, specially of the bones and is useful for oleation. [17]
Seasonal indications
Seasonal indications for different types of unctuous substances:
- Ghee is to be used in autumn (Sharath Rutu),
- Vasa and Majja (Fat and marrow) in the month of Vaishakha (April- may) and
- Taila – oil during the rainy(Pravrit) season.
- One should not take any of the oily substance when it is extremely hot or cold.[18]
Time for the administration of fats
In case of Vata and Pitta imbalance, Oleation Therapy should be administered in the evening.
When the Kapha is vitiated it is administered in mid-day.[19]
Complications of untimely administration of fats
If Oleation Therapy is administered during the day time in summer or to patients suffering from diseases dominated by the vitiation of Vata or Pitta, this may cause fainting, thirst, insanity or jaundice.
If one suffering from diseases of Kapha imbalance or from a disease during the course of the winter, if he is administered with oleation during evening, he will suffer from anaha (bloating), anorexia (aruchi), colic pain and anaemia. [20-21]

Anupana for unctuous substances
- Ghee is to be taken with the Anupana of hot water,
- oil with anupana of Yusha (vegetable soup),
- muscle fat and bone marrow with Anupana of Manda (thin gruel).
Or all these oily substances may be taken with the Anupana of hot water. [22]
Pravicharana Sneha
Sneha Pravicharana – Twenty four recipes of oils and fats:
The following are the 24 forms of preparation of unctuous substances:-
Odana (porridge),Vilepi (a type of gruel prepared with four times of water), Mamsarasa (meat soup), meat, milk, curd, Yavagu (a type of gruel prepared with six times of water), pulse, curry, vegetable soup, Kambalika (sour milk mixed with whey and vinegar), Khada (butter milk boiled with acid vegetables and spices), Saktu (roasted grain flour), pastry prepared of sesame , Liquor, Linctus, Bhakshya (foods that require hard chewing) Massage, Enema, Douche, Gandusha -Gargle, Karna taila – ear drop, Dhumapana – Inhalation,
preparation soothing to the ears and eyes.[23-25]
Importance of Acchapeya
Importance of Acchapeya – pure-fat administration:
The intake of simple (unmixed) oily substance is regarded by physicians as the best Oleation Therapy.[26]
Sneha Pravicharana combinations
Sneha Pravicharana – Classification of fat preparation combinations:
Oily preparations are of 63 types depending on their association with the drugs having six rasas (tastes) in isolation or variant combination. Together with the simple (unmixed) ones, these substances are of sixty four types. A physician, being expert with the habit, seasons, diseases and individual requirements should accordingly administer these sixty four types of preparations of fats and oils. [27-28]
Note: The term Sneha Pravicharana is used both for different forms of oil and fat administration and also for different types of oil and fat administration.

Dose schedule for fat administration
- The dose of the Oleation Therapy is of three types, depending upon the time taken for its digestion.
- The dose of oils and fats that require 24 hours for its digestion is of the first type (superior).
- The one requiring the whole day (12 hours) is of the second type (moderate) and
- The one requiring six hours only is of the third type (inferior).
Administration of oils and fats
Administration of oils and fats based on individual needs
Maximum dose
Indication for maximum dose of fats and oils (which digests in 24 hours)
Those who are in the habit of taking adequate quality of oils and fats and have resistance to hunger and thirst, whose digestion power is high, those who are themselves very strong, those suffering from
Gulma (abdominal tumour), snake bite, Visarpa (Skin diseases characterised with spread),
insanity, dysuria, constipation should use the first (that is superior) type of dose of Oleation Therapy (which would get digested in 24 hours).
The following are the effects of its intake. If properly administered, it alleviates all ailments instantaneously; it eliminates the Doshas, it strengthens all the systems of the body; it rejuvenates the body, sense organs and mind.
Moderate dose
Indication for moderate dose of fats and oils (which digests in 12 hours):
Those suffering from eruptions, boils, pimples, itching, papules, spreading type of skin disease, chronic urinary disorders and gout (Vatarakta); those who cannot eat much, those who are of laxed bowels and those with moderate strength are advised with fats and oils of moderate dose.
The Oleation Therapy, in this dosage, does not create much complications nor does it affect the strength too much.
Low dose
Indication for low dose of fats and oils (which digests in 6 hours):
The old, the children, those with tender health, those who have been brought up in luxury, those for whom evacuation of bowel is not good, those with weak digestion, chronic fever, diarrhoea and cough, and those who are very weak, are advised with low doses of oils and fats.
Benefits: This stimulates libido and gives strength. This is least harmful and can be administered for a long time. [29-40]

Indications for the administration of Ghee
Intake of herbal ghee is prescribed for those with
- Vata Pitta body type,
- Those suffering from Vata and Pitta imbalance disorders,
- Chakshu Kama – those desiring good eye sight,
- Kshata Ksheena – with chest injured,
- For the old, children and weak,
- Those desirous of longevity, of strength, good complexion, voice, nourishment, progeny, tenderness, luster, Ojas, memory, intelligence, power of digestion, wisdom, proper functioning of sense organs and
- Those afflicted with injuries due to burns, by weapons, poisons and fire.[41-43]
Indications for the administration of oils
Intake of oil is prescribed even in the winter for
- Those who are having Kapha in excess,
- Those who have excess fat in throat and abdomen,
- Those suffering from Vata imbalance diseases and
- Those desirous of strength, slimness, lightness, sturdiness, steadiness, tenderness and smoothness of the skin, those having worms and other infection in their bowels,
- Those having Krura koshta (unpredictable bowel – sometime soft, most of the times hard)
- Those afflicted with wound sinuses and those who are accustomed to the intake of oil. [44-46]
Indications for the administration of muscle fat
Intake of muscle fat is prescribed for
- Those who can stand the wind and the sun,
- Those with rough skin
- Those who are emaciated due to the bearing of heavy loads or exertion from long walks,
- Those with depleted semen and blood
- Those with less Kapha and Medas (fat)
- Those having excruciating pain, in bone joints, veins, ligaments, vital organs, abdominal viscera,
- Those whose channels of circulation are affected by strong Vata,
- Those with excellent digestion strength and those who are accustomed to the intake of fats.
- This is, however, to be administered only to such patients as are required to be given Oleation Therapy. [47-49]

Indications for the administration of bone marrow
The intake of bone marrow is prescribed for
- Those who have strong digestive power
- Those who can withstand stress and strain, greedy eaters,
- Those accustomed to the intake of oils and fats,
- Those afflicted with Vata and those with hard bowel.
- This is, however, to be administered only to such patients who are required to be given oleation therapy.
Thus, the indications for different types of oleation therapy useful for different types of patients have been explained. [50]
Course for fat administration before Panchakarma
Minimum period is 3 days.
Maximum period is 7 days. [51]
General indications for Fat/Oil therapy
Oleation therapy in general is prescribed for
- Those who are to be given Swedana (sweating treatment) or Panchakarma therapy
- Those who have roughness in the skin
- Those suffering from diseases due to Vata imbalance
- Those who indulge in physical exercise, wine and women
- Those who suffer from mental strain.[52]
Contra- indications for fat administration
Oleation Therapy should not be administered to such of the patients
- Who are eligible for Rukshana(Drying Therapy)
- To those in whom Kapha and Medas (fat) are aggravated
- Those with Kapha symptoms like excess mucus secretion from mouth and anus
- Those whose power of digestion is continuously weak
- Those suffering from thirst and fainting
- The pregnant women
- Those with dry palate
- Those having aversion to food
- Those suffering from vomiting
- Abdominal diseases
- Diseases due to improper digestion as well as metabolism
- Those afflicted with Gara type of poison (chronic diet-poison),
- The weak, emaciated, those having aversion to the intake of unctuous substances
- Those intoxicated and those being administered inhalation and enema therapies.
If Oleation Therapy is administered to such persons, they re likely to fall victims of disastrous complications[53-56]
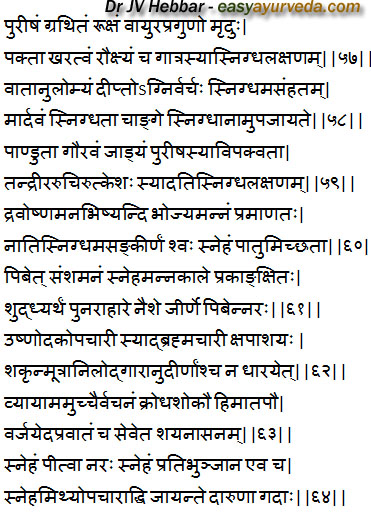
Signs and symptoms of Incomplete Oleation
Hard and dry stool, derangement of Vayu, weak digestion power, roughness and dryness of the skin are the signs of under oleation [57]
Signs and symptoms of Proper Oleation
Evacuation of the flatus, good digestive power, untucous and soft stool, tenderness and smoothness of the body are the signs of proper oleation.[58]
Signs and symptoms of Over Oleation
Paleness, heaviness, stiffness, stool indicative of indigestion, drowsiness, anorexia are the signs of over oleation.[59]
Pre-Oleation management
A day preceding the administration of Oleation Therapy:
- One should take food in proper quantity.
- The food should be liquid, hot and Anabhisyandi (that does not obstruct the channel of circulation / that which does not leave a coating on body channels).
- It should neither be too unctuous nor a mixture of two opposite qualities (hot and cold).
- When hungry, one should take alleviation (samshamana) type of oleation therapy in low doses, during lunch hours.
- Samsodhana type of oleation therapy should be administered when the food taken in the preceding night has been well digested.[60-61]
Management during oleation
While under the oleation therapy, one should always
- Use hot water
- Observe Brahmacharya
- One should not sleep during day time
- One should not suppress urges of motion, urination, flatus eructation, etc.
- One should avoid physical exercise, loud speech, anger, anxiety, cold and sun
- One should lie down or sit in a place well protected from wind.
- Even after the completion of the course of oleation therapy one might be required to take some more unctuous substance of homologous qualities.
- Adoption of wrong regimen during the course of Oleation Therapy will result in serious complications[62-64]
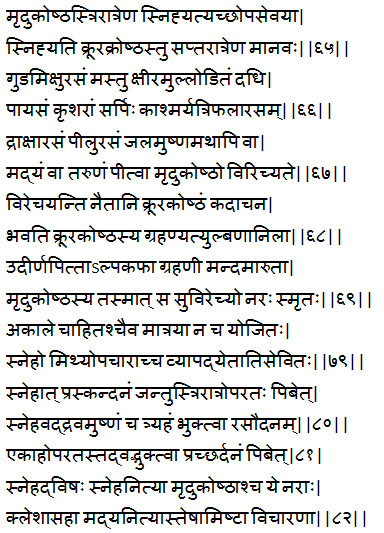
Test to identify Mridu Koshta
Therapeutic test for the diagnosis of Mridu Koshta (laxed bowel):
A person with Mridu Koshta (laxed bowel), is properly oleated by taking an unctuous substance for three consecutive nights and one with Krura Koshta (costive bowels) for seven consecutive nights.
People with mridu koshta would have purgation with following –
Sugar candy, sugarcane juice, mastu(whey), milk cream from the curd, curd, payasa (milk preparation), gruel made from sesame, rice and black gram, ghee, juice of Kashmarya (Gmelina arborea Linn), Haritaki – (Chebulic Myrobalan), Amla, Bibhitaki (Terminalia belerica Roxb), raisins and Pilu (Salvadora persica Linn), even hot water or fresh wine.
But these can not produce purgative effect for those with Krura Koshta (costive bowel) because their intestine is too much dominated by Vata, Purgation is easy for those with laxed bowel, because their Grahani is dominated by Pitta and is least affected by Kapha and Vata. [65-69]
Side effects of oleation and its management
Unctuous substances taken by a person with Pitta imbalance in duodenum and having strong digestive power, gets digested quickly by virtue of the power of the digestive fire.
Strong digestive fire, having consumed the heavy dose of unctuous substance displaces the Ojas and aggravates the thirst with complications.
Even very heavy food is not enough to satisfy the digestive fire excited by oleation.
In the circumstances, unless he takes recourse to cold water, the patient may die as a serpent lying in the midst of a heap of wood dies with the fire of its own poisonous breath.
If a patient gets thirst due to indigestion of the unctuous substances taken, the physician should administer vomiting treatment (Vamana)
The patient should again be given Vamana after being given cold water and unctuous food.
Unmixed ghee should not be taken in the event of the domination of Pitta specially when Pitta is associated with Ama.
Ghee taken in this condition brings about paleness (Jaundice) in the body and may prove to be fatal by impairing the consciousness.
If Oleation Therapy is not administered properly, drowsiness, Nausea, Acute constipation, Fever, stiffness, Unconsciousness, spreading type of skin disease, Pruritus, Paleness, Oedema, Piles, Anorexia, Thirst, Obstinate abdominal diseases due to the malfunctioning of the intestine including duodenum, Stillness, Suppression of speech, Colic pain and diseases due to improper digestion and metabolism will occur.
In that case Vamana, Swedana (sweating) or fasting (till the previous intake of Unctuous substance gets digested) is prescribed.
Purgation may also be administered with due regard to the strength of the disease depending on individual cases. Complications arising out of the inappropriate oleation may also be neutralized by the intake of Takrarista (Charaka Chikitsa 14:72-75), unctuous drink and food, urine, Triphala Churna [70-78]
The Oleation Therapy gives rise to many complications, if it is administered at inappropriate times or is not taken in the proper dose or taken in excess or (even if taken properly but) followed by improper regimen.[79]
Virechana (Purgation) is to be administered three days after the completion of the oleation therapy. During food prescribed during this interval of three days, the patient should take unctuous liquid and hot porridge together with meat juice.[80]
The Vamana (vomiting treatment) is to be administered one day after the completion of the oleation therapy. The food prescribed during this interval of one day is the same as indicated in the preceding verse.
The regimen prescribed in connection with the purgation are to be followed with regard to the alleviation type of oleation therapy also.[81]
Indications for the administration of fat preparation
Unctuous preparations rather than pure unctuous substances are to be prescribed for persons who have aversion of taking unctuous substance, those who are in the habit or regularly taking, unctuous substances, wine, those with Mridu Koshta (laxed bowels) and those who cannot resist to physical strain. [82]
The meat juice of Lava (Common quail), Tittira (black partridge), Mayura (peacock), Hamsa (swan), Varaha (Pig), Kukkuta (red squr fowl), Go (Cow), Aja (Goat), Aurabhra (wild sheep) and fish are useful in oleation.
The drugs required to be mixed with meat juice are
Yava – Barley (Hordeum vulgare), Kola( Zizyphus jujube Lam), Kulattha(Dolichos Biflorus Linn), Sugar candy, Crystal sugar, Dadima – Pomegranate, , Sunthi (Zingiber officinale Rosc), Pippali – Long pepper fruit – Piper longum (piper longum Linn) and Maricha – Black pepper fruit – piper nigrum (Piper nigrum Linn).
If sesame seeds together with unctuous substances, Phanita (A preparation of sugar cane), Krishara (a type of gruel) added with sufficient quantity of unctuous substance and Kambalika (sour milk mixed with whey and vinegar) prepared with sesame seed, are taken before meals, they are useful in oleation.
One having dryness should take Phanita (a prepartion of sugar cane), ginger juice and oil together with wine. After they have been digested he should take his meal with minced meat.
A person with Vata body type can be oleated by taking oil, together with the upper portion of wine, muscle fat, marrow milk and Phanita (a preparation of sugar cane).
One gets oleated by taking warm milk fresh from the cow mixed up with sugar and unctuous substance or cream of the curd along with Phanita.
Pancha Prasritaki Peya – type of gruel prepared with milk and black gram and added with unctuous substance in sufficient quantity oleates immediately. Pancha prasritaki Peya is prepared with ghee, oil, muscle fat, marrow and rice- Prarita(96 g) of each. This is prescribed for one in need of oleation therapy.
Juice of pork made unctuous by adding ghee and salt, if taken properly twice a day oleates immediately.[83-90]
Specific Contra- Indications of Substances used in oleation Therapy
One suffering from a spreading type of skin disease, oedema and obstinate urinary disorders should not use meat juice of domestic, marshy and aquatic animals, sugar candy, curd, milk and sesame seeds.
If necessary, such patients should be oleated by means of ghee duly prepared with therapeutically useful during or with Pipali – long pepper, Haritaki and Triphala.
A physician should prepare an unctuous drink with the juice of Raisin, and Amalaki (Emblica officinalis Gaertn), sour curd, ginger, long pepper and black pepper. By taking this, one gets oleated.
The medicated ghee best suited for the purpose of oleation therapy is to be prepared with the decoction of Barley, jujube, horse gram, Alkalies, Wine, curd and ghee prepared out of milk. [91-94]
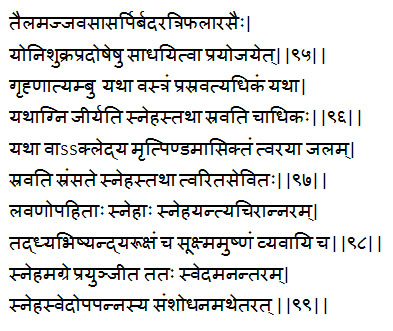
Oleation therapy in genital disorders
Therapeutic preparation for oleation in the treatment of diseases of the female genital tract and semen is to be made with oil, marrow, muscle fat, ghee and the decoction of Badara – Zizyphus jujuba Lam, Triphala. [95]
Sadya Snehana – Simile
Sadya Snehana – Simile regarding the effect of quick oleation:
As a cloth absorbs certain amount of water but oozes out the water in excess, so the oleation therapy used just in proportion with the digestive powder gets digested (that is, it is ineffective for the purpose of oleation); It oleates only when it is administered in excess. Or as water poured on a cold earth pot in quick succession oozes out after slightly saturating the latter, so, oleation therapy administered in quick succession in a day, goes waste without oleating properly. [96-97]
Salt in Sadyo Snehana
Role of salt in Sadyo Snehana – quick oleation:
Unctuous drink prepared with salt oleates an individual instantaneously because salt is by nature Abhisyandi (that obstructs the channel of circulation), unctuous, Sukshma (that passes through subtle channels), hot, Vyavayi (which gets digested only after its absorption and perversion in the whole body).[98]
Routine for administration
Routine for the administration of different therapeutic measures:
Oleation therapy is required to be administered first; then sweating therapy is to be applied; finally elimination therapy is to be administered after the administration of oleation and fomentation.[99]
To sum up:-
Lord Punarvasu has described in response to the question, the various types of oleation, the procedure for oleation, all the related complications and the preparations of various drugs useful for this therapy.[100]
Thus ends the Thirteenth Chapter on “Oleation” of Sutra section of Agnivesha’s work as redacted by Charaka.









4 comments on “Snehadhya Charak Samhita Sutrasthan 13th Chapter: Snehakarma”
shaju kalarickal
Dear Dr.Hebbar.thankyou for all your articles….its so great…..
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
welcome! I am glad you find them helpful. 🙂
Dr.G.SivaRam
Glycyrrhiza glabra is not included in the source of oils by charaka. It is Madhuuka (Madhuca indica). Please correct it.
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
Thanks. Corrected.